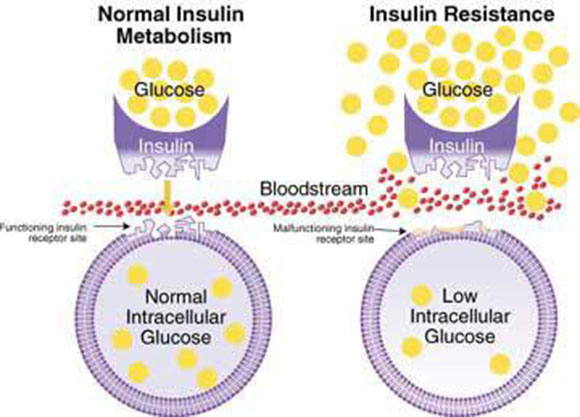
Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body produces insulin but does not use it effectively. When people have insulin resistance, glucose builds up in the blood instead of being absorbed by the cells, leading to type 2 diabetes or prediabetes.
Most people with insulin resistance don’t know they have it for many years—until they develop type 2 diabetes, a serious, lifelong disease. The good news is that if people learn they have insulin resistance early on, they can often prevent or delay diabetes by making changes to their lifestyle.
What causes insulin resistance?
Although the exact causes of insulin resistance are not completely understood, scientists think the major contributors to insulin resistance are excess weight and physical inactivity.
Excess Weight: Some experts believe obesity, especially excess fat around the waist, is a primary cause of insulin resistance. Scientists used to think that fat tissue functioned solely as energy storage. However, studies have shown that belly fat produces hormones and other substances that can cause serious health problems such as insulin resistance, high blood pressure, imbalanced cholesterol, and cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Belly fat plays a part in developing chronic, or long-lasting, inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation can damage the body over time, without any signs or symptoms. Scientists have found that complex interactions in fat tissue draw immune cells to the area and trigger low-level chronic inflammation. This inflammation can contribute to the development of insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and CVD. Studies show that losing the weight can reduce insulin resistance and prevent or delay type 2 diabetes.
Physical Inactivity: Many studies have shown that physical inactivity is associated with insulin resistance, often leading to type 2 diabetes. In the body, more glucose is used by muscle than other tissues. Normally, active muscles burn their stored glucose for energy and refill their reserves with glucose taken from the bloodstream, keeping blood glucose levels in balance.
Studies show that after exercising, muscles become more sensitive to insulin, reversing insulin resistance and lowering blood glucose levels. Exercise also helps muscles absorb more glucose without the need for insulin. The more muscle a body has, the more glucose it can burn to control blood glucose levels.
Other Causes: Other causes of insulin resistance may include ethnicity; certain diseases; hormones; steroid use; some medications; older age; sleep problems, especially sleep apnea; and cigarette smoking.




